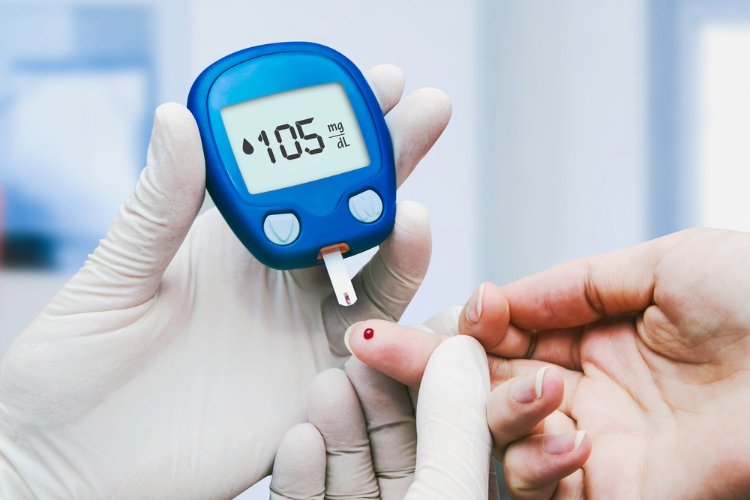
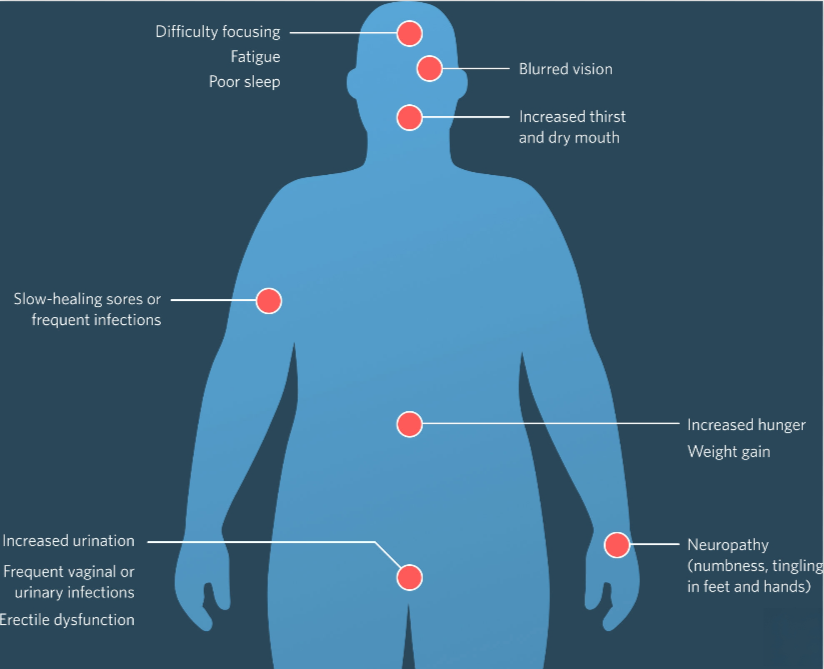
Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes symptoms vary depending on blood sugar levels. Some individuals may experience mild or no symptoms at all. However, recognizing early warning signs can be life-saving. Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent Urination
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing wounds or infections
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is categorize into several types, each with unique causes and characteristics.
Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes happens when the immune system harms the cells in the pancreas that make insulin. This results in little to no insulin production. People with Type 1 diabetes require daily insulin injections to regulate their blood sugar levels. The exact cause is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors may play o role.
Type 2 Diabetes:
This is the most common form of diabetes, often linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, obesity and physical inactivity. In this case the body does not use insulin correctly or makes too little of it. It usually gets managed by changing diet and exercise habits taking medicine or sometimes adding insulations
Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes appears during pregnancy when the body fails to produce insufficient insulin for increased demands. The condition often stops after birth but may raise the risk of Type 2 diabetes later in life. Good prenatal care, a proper diet plus exercise ease this problem.
Prediabetes:
Prediabetes happen when blood sugar remains above normal yet stays below the level of Type 2 diabetes. Changes in lifestyle such as a balanced diet plus physical activity, may prevent or postpone Type 2 diabetes.
For more details, visit: What is Diabetes?
Causes of Diabetes
Diabetes can be caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Here are some key contributors:
Genetic Factors
A family record of diabetes lifts the chance of getting the disease. Some genes may make a person more likely to have trouble with insulin or have an immune reaction that leads to diabetes.
Poor Diet and Obesity
Eating many processed foods, sweet drinks plus unhealthy fats leads to extra body weight and insulin problems, which raises the odds of Type 2 diabetes.
Physical Inactivity
A life with little movement cuts down how well insulin works, which makes it more difficult for the body to control blood sugar well. Daily exercise cuts the chance of diabetes.
Autoimmune Response
Type 1 diabetes happens when the immune system wrongly harms insulin cells in the pancreas. Both family traits and environmental factors seem to play a part.
Hormonal Changes During Pregnancy
Shifts in hormones when pregnant may trigger gestational diabetes. If not managed properly, it might cause problems for both mother and baby.
Learn more about causes of diabetes
Treatment of Diabetes
Managing diabetes requires changes in daily habits, use of medicine plus regular checks. The choice of treatment depends on the kind and seriousness of diabetes.
1. Healthy Diet
A balanced diet that includes fiber, lean proteins, good fats as well as whole grains helps keep blood sugar stable. Do not eat processed food, too much sugar or bad fats.
2. Regular Exercise
Regular physical work boosts the body’s response to insulin and keeps blood sugar steady. Jog, ride a bike or work with weights as these help a lot.
3. Medication and Insulin Therapy
People with Type 1 diabetes or some with Type 2, must use insulin injections or a pump to manage blood sugar. Doctors may also give other medicine like metformin for Type 2.
4. Blood Sugar Monitoring
Checking blood sugar often shows progress and stops problems. Use a device that keeps continuous measures or one that you check by hand to hit the target range.
5. Stress Management
Chronic stress can increase blood sugar levels. Practicing mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation techniques can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
6. Weight Management
Staying near a healthy weight lowers the chance of Type 2 and helps those with diabetes manage it better. Losing even a small bit of weight can lift blood sugar control.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a serious but manageable condition. With the right lifestyle choices, medical treatment, and regular monitoring, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. Early detection and proactive management are key to preventing complications and maintaining overall well-being. For more insights on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, check out our article on why health and fitness are so important.