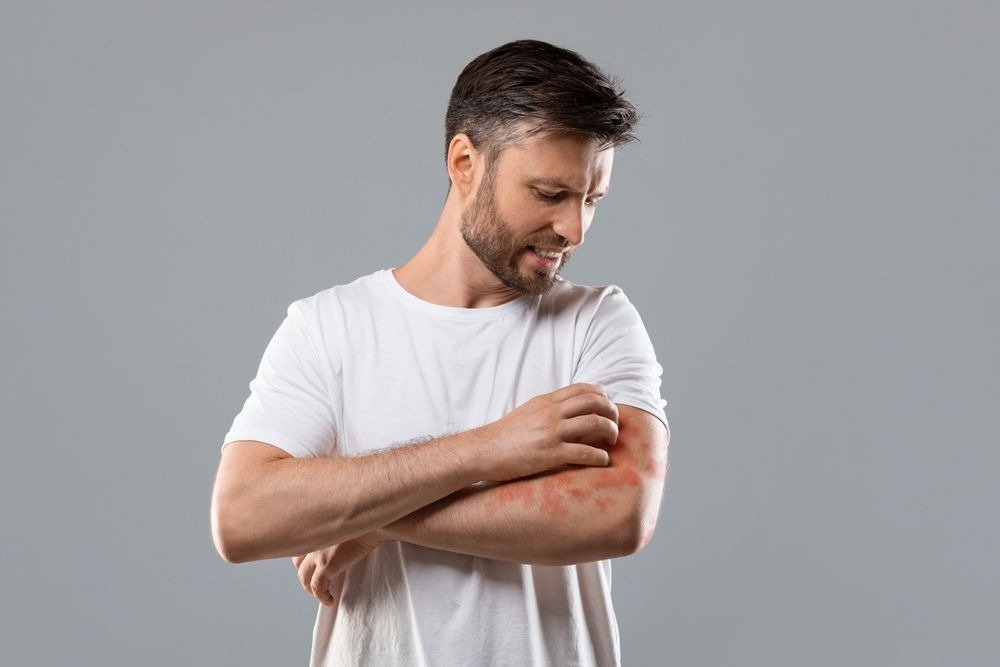
If you’ve ever wondered what is eczema, you’re not alone. Millions of people globally experience itchy, inflamed, and uncomfortable skin due to this chronic condition. Eczema can range from mild dryness to severe flare-ups that disrupt daily life. In this post, we’ll explore what eczema is, its common causes, symptoms, and the most effective natural remedies you can use at home to manage it.
What Is Eczema?
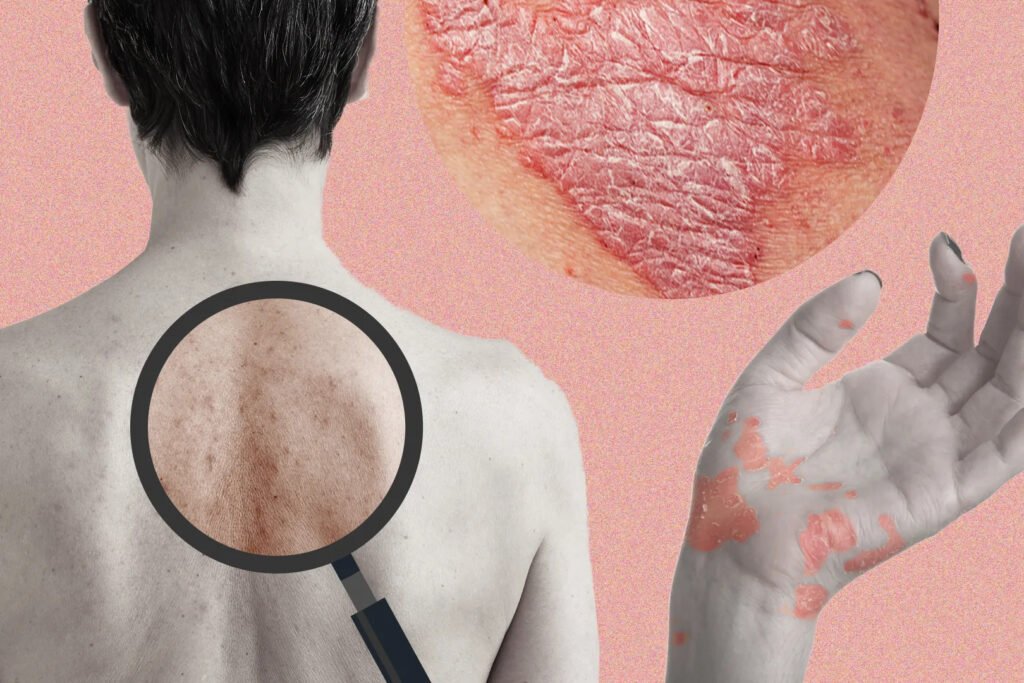
Eczema, medically known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition. It causes patches of dry, red, and itchy skin that can become cracked or weepy during flare-ups. Eczema affects both children and adults and often runs in families.
What Causes Eczema?
There’s no single cause of eczema, but researchers believe it develops due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Main triggers include:
- Weakened skin barrier function
- Allergens like pollen, pet dander, and dust mites
- Chemical irritants in soaps, cosmetics, and detergents
- Extreme weather conditions
- Stress and hormonal changes
- Dietary triggers (e.g., dairy, gluten, soy for some people
For more on eczema triggers, check this detailed guide from Nationaleczema
What Are the Symptoms of Eczema?
Eczema symptoms may differ based on age and severity but typically include:
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Red or brownish-gray skin patches
- Dry, cracked, or scaly skin
- Fluid-filled blisters
- Crusting or thickened skin after repeated scratching
Read our blog on 10 Foods to Boost Your Immune System Naturally to support your skin health from within.
Types of Eczema
Understanding the different types of eczema is crucial for accurate treatment and symptom management. While many people use the term “eczema” generally, it actually refers to a group of skin conditions. Let’s explore the most common types:
1. Atopic Dermatitis
This is the most common form when people ask, what is eczema. It often begins in childhood and is associated with asthma or hay fever. Symptoms include dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, especially in the creases of the arms, knees, and neck.
2. Contact Dermatitis
This occurs when the skin reacts to a substance it touches—such as soap, detergent, or metal. It’s divided into allergic and irritant contact dermatitis.
3. Dyshidrotic Eczema
Characterized by tiny, fluid-filled blisters on the hands and feet, often caused by stress, allergens, or exposure to water and metals.
4. Nummular Eczema
This type appears as circular, coin-shaped spots, usually on the arms or legs. It’s triggered by dry skin or skin injuries and can be very itchy.
5. Seborrheic Dermatitis
Often found on oily areas like the scalp, face, and chest, this type causes red, scaly patches and dandruff. Though often mild, it can become chronic.
6. Stasis Dermatitis
Common in older adults with poor circulation, especially in the lower legs. It causes swelling, redness, and skin irritation due to fluid buildup under the skin.
Each type of eczema may require a different care approach. Knowing which kind you have helps in finding the right treatment and avoiding triggers.
Natural Remedies for Eczema
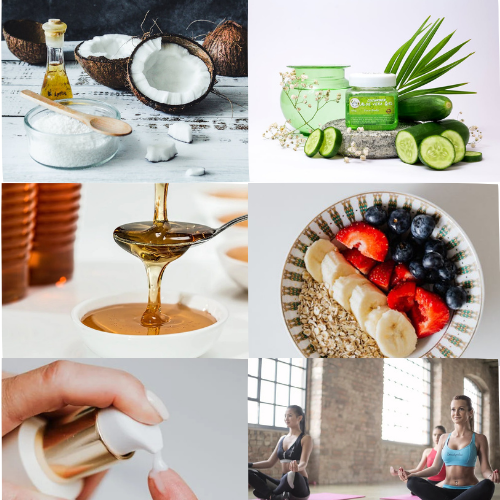

Instead of relying solely on medicated creams, many people find relief with natural remedies that soothe inflammation and repair the skin barrier. Here’s what works:
1. Coconut Oil
Its antimicrobial and moisturizing properties make virgin coconut oil a top natural remedy. Apply it twice a day for relief.
2. Aloe Vera Gel
Pure aloe Vera offers cooling relief, reduces itching, and helps with skin regeneration.
3. Oatmeal Baths
Colloidal oatmeal has anti-inflammatory effects. Add it to lukewarm baths to reduce itchiness and redness.
4. Honey
A natural antibacterial agent, honey can be applied to small eczema patches for its healing and anti-inflammatory effects.
5. Fragrance-Free Moisturizers
Apply within 3 minutes of bathing to lock in moisture and support your skin barrier.
6. Stress Management
Eczema flare-ups often follow periods of high stress. Incorporate yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to reduce tension.
Want more? Read this insightful article
How to Care for Eczema-Prone Skin Daily
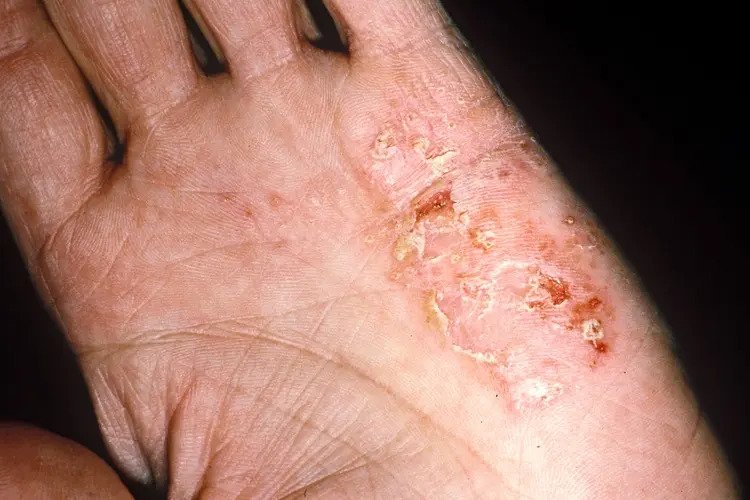
- Use mild, unscented soaps and detergents
- Keep baths short and avoid hot water
- Always moisturize after washing
- Wear breathable, cotton fabrics
- Avoid scratching to prevent infection
When to See a Doctor
If your eczema becomes severe, infected, or does not improve with home remedies, consult a dermatologist. Prescription-strength creams or oral medications may be needed.



